What are Derivatives? Derivatives Kya Hote Hai? Simple Explanation in Hindi
What is Derivation?
What are Derivatives? Derivatives Kya Hote Hai? Simple Explanation in Hindi. A derivative is a financial instrument that derives its value from an underlying asset, index, reference rate, or another financial instrument. Derivatives are contracts between two or more parties, and their value changes in response to changes in the value of the underlying asset or factor.
Derivatives as financial instruments depend upon underlying assets for their value. These instruments have been traded in markets throughout the ages. The history of Derivatives trading has step by step evolved in range and complexity, laying down what would become the foundation of the modern trade in Derivatives that started in the 1970s.
What is Derivation? It seems like you’re asking about “derivation.” In the context of trading and finance, the term “derivation” is not commonly used. However, I’m assuming you might be referring to “derivative” or “derivatives.”
What are Derivatives? Derivatives Kya Hote Hai? Simple Explanation in Hindi A derivative is a financial instrument that derives its value from an underlying asset, index, reference rate, or another financial instrument. Derivatives are contracts between two or more parties, and their value changes in response to changes in the value of the underlying asset or factor.
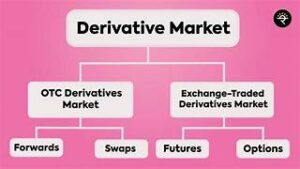
There are several types of derivatives, including:
- Options: Contracts that give the holder the right (but not the obligation) to buy or sell an underlying asset at a specified price (strike price) within a certain time frame. This includes call options and put options.
- Futures Contracts: Agreements to buy or sell an asset at a predetermined price on a specific future date. Futures contracts are standardized and traded on exchanges.
- Forwards: Similar to futures contracts, but forwards are customizable agreements between two parties. They are not traded on exchanges and are often used for specific, non-standardized needs.
- Swaps: Financial agreements in which two parties agree to exchange cash flows or financial instruments based on a certain set of conditions. Common types include interest rate swaps and currency swaps.
- Futures Options: These are options on futures contracts, giving the holder the right to buy or sell a futures contract at a specific price.
Derivatives ky hote hai ? are used for various purposes in the financial markets, including risk management, speculation, and hedging. They allow investors and traders to gain exposure to price movements without owning the underlying asset. However, it’s important to note that derivatives can be complex and involve a level of risk due to leverage and potential for significant price changes in the underlying assets or factors.
What are Derivatives? Derivatives Kya Hote Hai?Simple Explanation in Hindi If you have a specific context in which you’re using the term “derivation,” please provide more information so that I can assist you more accurately.
It seems like you’re asking about the term “derivation.” In the context of mathematics, particularly calculus, a derivation refers to the process of finding the rate of change of a function’s output with respect to changes in its input. What are Derivatives? Derivatives Kya Hote Hai? Simple Explanation in Hindi In other words, it involves calculating the slope of the function’s graph at a specific point.
What are Derivatives? Derivatives Kya Hote Hai? Simple Explanation in Hindi. The primary concept associated with derivation is the derivative. The derivative of a function represents how the function’s output value changes when its input value is changed by a small amount. Mathematically, the derivative of a function f(x) with respect to its input variable x is denoted as f'(x) or dy/dx.
Here’s a basic explanation of the derivative and the process of derivation:
- Definition of Derivative: Given a function f(x), the derivative f'(x) at a specific point x measures the instantaneous rate of change of the function at that point. It tells you how much the output of the function changes as the input changes by a tiny amount.
- Derivation Process: To find the derivative of a function, you apply differentiation rules. These rules provide formulas for finding the derivative of common types of functions, such as power functions, exponential functions, trigonometric functions, and more.
- Differentiation Rules: Differentiation rules include the power rule, product rule, quotient rule, chain rule, and rules for different types of functions. These rules allow you to find the derivative of a more complex function by breaking it down into simpler parts.
- Interpretation: The derivative has several interpretations, including:
- Slope: The derivative represents the slope of the tangent line to the function’s graph at a specific point. The steeper the slope, the faster the function is changing.
- Instantaneous Rate of Change: The derivative gives the rate at which the function’s output is changing at that specific point.
- Velocity and Acceleration: In the context of physics, derivatives can represent velocity (derivative of position) and acceleration (derivative of velocity).
- Applications: Derivatives have wide-ranging applications in mathematics, physics, engineering, economics, and other fields. They are used to solve optimization problems, model real-world phenomena, analyze changes in quantities, and more.
- Higher Derivatives: The process of finding derivatives can be repeated, resulting in higher derivatives (second derivative, third derivative, and so on). Higher derivatives provide information about the rate of change of the rate of change, and so on.
What are Derivatives? Derivatives Kya Hote Hai? Simple Explanation in Hindi In essence, derivation involves finding the derivative of a function, which quantifies how the function changes as its input changes. This process is fundamental in calculus and plays a crucial role in understanding how quantities vary in mathematical models and real-world situations.
Follow On Youtube :- https://youtu.be/Bt7Up1XdiLQ?si=kwf-Jd5OaTt-ChAV
What are Derivatives? Derivatives Kya Hote Hai? Simple Explanation in Hindi In the context of the stock market or finance, the term “derivation” is not commonly used. However, I believe you might be referring to “derivative” instruments. Let me provide an explanation of derivatives in the context of the stock market:
Derivatives in the Stock Market:
What are Derivatives? Derivatives Kya Hote Hai? Simple Explanation in Hindi Derivatives are financial instruments that derive their value from an underlying asset, such as stocks, bonds, commodities, or market indices. They allow investors and traders to speculate on price movements or manage risk without directly owning the underlying asset. Derivatives are traded on various exchanges and over-the-counter (OTC) markets. What are Derivatives? Derivatives Kya Hote Hai? Simple Explanation in Hindi
There are several types of derivatives used in the stock market:
- Options: Options are contracts that give the holder the right, but not the obligation, to buy (call option) or sell (put option) an underlying asset at a predetermined price (strike price) on or before a specific expiration date. Options are often used for hedging, speculation, and generating income.
- Futures Contracts: Futures contracts obligate the buyer to purchase and the seller to sell an underlying asset at a specified price on a predetermined future date. Futures are used for speculation and hedging against price fluctuations.
- Forwards: Similar to futures contracts, forwards are customized agreements between two parties to buy or sell an asset at a future date and at a predetermined price. Forwards are not standardized and are often used for specific needs.
- Swaps: Swaps involve the exchange of cash flows or financial instruments based on certain conditions. In the context of stocks, equity swaps allow parties to exchange returns on stocks without transferring ownership.
Derivatives can serve various purposes in the stock market:
- Hedging: Investors use derivatives to protect their portfolios from adverse price movements. For example, a portfolio manager might use index futures to hedge against a potential market decline.
- Speculation: Traders can speculate on the price movements of underlying assets without owning them. For instance, an options trader might purchase call options if they expect a stock’s price to rise.
- Arbitrage: Derivatives can be used for arbitrage opportunities, where traders exploit price discrepancies between related assets or markets.
- Leverage: Derivatives allow traders to control a larger position with a smaller initial investment, potentially amplifying gains but also losses.
- Income Generation: Options strategies like covered calls can be used to generate income from existing stock holdings.
It’s important to note that while derivatives offer various benefits, they also carry risks due to leverage, market volatility, and potential for significant price movements. What are Derivatives? Derivatives Kya Hote Hai? Simple Explanation in Hindi Investors and traders should have a solid understanding of the derivative instruments they are trading and the associated risks.
Types of Derivations
What are Derivatives? Derivatives Kya Hote Hai? Simple Explanation in Hindi It seems there might be some confusion regarding the term “derivations” in the stock market context. In the stock market, the term “derivatives” is used to refer to financial instruments that derive their value from an underlying asset. These instruments include options, futures, forwards, and swaps, as mentioned in previous responses. However, if you are looking for something else related to stock market analysis, here are some common analytical techniques that traders and investors use:
- Technical Analysis:
- Moving Averages: Averages of an asset’s prices over a specific period, used to identify trends and potential reversal points.
- Relative Strength Index (RSI): A momentum indicator that measures the speed and change of price movements.
- MACD (Moving Average Convergence Divergence): Compares two moving averages to identify potential changes in momentum.
- Bollinger Bands: Volatility bands placed above and below a moving average to indicate potential price levels.
- Fundamental Analysis:
- Earnings Per Share (EPS): Measures a company’s profitability by dividing its earnings by the number of outstanding shares.
- Price-to-Earnings Ratio (P/E): Compares a company’s stock price to its earnings per share, indicating whether the stock is overvalued or undervalued.
- Dividend Yield: Measures the annual dividend income an investor can expect to receive relative to the stock’s price.
- Book Value: The value of a company’s assets minus its liabilities, divided by the number of outstanding shares.
- Quantitative Analysis:
- Algorithmic Trading: Using computer algorithms to make trading decisions based on predefined criteria.
- Statistical Models: Using statistical techniques to forecast stock prices or market trends.
- Sentiment Analysis:
- Social Media Analysis: Monitoring social media platforms to gauge public sentiment about specific stocks or the market as a whole.
- News Analysis: Assessing news articles and headlines for potential impacts on stock prices.
- Seasonal Analysis:
- Calendar Effects: Studying historical price patterns that tend to recur during certain times of the year, month, or week.
- Economic Indicators:
- GDP Growth: The rate at which a country’s economy is growing or contracting.
- Unemployment Rate: The percentage of people in the workforce who are unemployed.
- Interest Rates: Central bank policies that affect borrowing costs and overall economic activity.
What are Derivatives? Derivatives Kya Hote Hai? Simple Explanation in Hindi It’s important to note that these techniques are not “derivations” but rather tools and methods used for analyzing stocks and making informed investment decisions. Different investors and traders may use a combination of these techniques to suit their strategies and risk tolerance.
A derivative is a financial instrument that derives its value from an underlying asset, index, reference rate, or another financial instrument. Derivatives are contracts between two or more parties, and their value changes in response to changes in the value of the underlying asset or factor.
What are Derivatives? Derivatives Kya Hote Hai? Simple Explanation in Hindi The term derivative refers to a type of financial contract whose value is dependent on an underlying asset, group of assets, or benchmark. A derivative is set between two or more parties that can trade on an exchange or .
These contracts can be used to trade any number of assets and carry their own risks. derive from fluctuations in the underlying asset. These financial securities are commonly used to access certain markets and may be traded to against risk. Derivatives can be used to either mitigate risk (hedging) or assume risk with the expectation of commensurate reward (speculation). Derivatives can move risk (and the accompanying rewards) from the What are Derivatives? Derivatives Kya Hote Hai? Simple Explanation in Hindi
KEY TAKEAWAYS
- Derivatives are financial contracts, set between two or more parties, that derive their value from an underlying asset, group of assets, or benchmark.
- A derivative can trade on an exchange or over-the-counter.
- Prices for derivatives derive from fluctuations in the underlying asset.
- Derivatives are usually leveraged instruments, which increases their potential risks and rewards.
- Common derivatives include futures contracts, forwards, options, and swaps.
Understanding Derivatives
A derivative is a complex type of financial security that is set between two or more parties. What are Derivatives? Derivatives Kya Hote Hai? Simple Explanation in Hindi Traders use derivatives to access specific and trade different assets. Typically, derivatives are considered a form of advanced investing. The most common underlying assets for derivatives are stocks, bonds, , interest rates, and market indexes. Contract values depend on changes in the prices of the underlying asset.
Derivatives can be used to hedge a position, speculate on the directional movement of an underlying asset, or give leverage to holdings. These assets are commonly traded on exchanges or OTC and are purchased through brokerages. The is among the world’s largest derivatives exchanges.1
It’s important to remember that when companies hedge, speculating on the price of the commodity .What are Derivatives?Derivatives Kya Hote Hai? Simple Explanation in Hindi Instead, the hedge is merely a way for each party to manage risk. Each party has its profit or margin built into the price, and the hedge helps to protect those profits from being eliminated by market moves in the price of the commodity.
What are Derivatives? Derivatives Kya Hote Hai? Simple Explanation in Hindi OTC-traded derivatives generally have a greater possibility of which is the danger that one of the parties involved in the transaction might . These contracts trade between two private parties and are unregulated. To hedge this risk, the investor could purchase a currency derivative to lock in a specific exchange rate. Derivatives that could be used to hedge this kind of risk include and
Types of Derivatives
Derivatives today are based on a wide variety of transactions and have many more uses. There are even derivatives based on weather data, such as the amount of rain or the number of sunny days in a region.
There are many different types of derivatives that can be used for risk management, speculation, and leveraging a position. The derivatives market is one that continues to grow, offering products to fit nearly any need or risk tolerance.
There are two classes of derivative products: “lock” and “option.” Lock products (e.g., futures, forwards, or swaps) bind the respective parties from the outset to the agreed-upon terms over the life of the contract. Option products (e.g., stock options), on the other hand, offer the holder the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell the underlying asset or security at a specific price on or before the option’s expiration date. The most common derivative types are futures, forwards, swaps, and options.
Futures
A what are Derivatives? Derivatives Kya Hote Hai? Simple Explanation in Hindi , or simply futures, is an agreement between two parties for the purchase and delivery of an asset at an agreed-upon price at a future date. Futures are standardized contracts that trade on an exchange. Traders use a futures contract to hedge their risk or speculate on the price of an underlying asset. The parties involved are obligated to fulfill a commitment to buy or sell the underlying asset.
For example, say that on Nov. 6, 2021, Company A buys a futures contract for oil at a price of $62.22 per barrel that expires Dec. 19, 2021. The company does this because it needs oil in December and is concerned that the price will rise before the company needs to buy. Buying an oil futures contract hedges the company’s risk because the seller is obligated to deliver oil to Company A for $62.22 per barrel once the contract expires. Assume oil prices rise to $80 per barrel by Dec. 19, 2021. Company A can accept delivery of the oil from the seller of the futures contract, but if it no longer needs the oil, it can also sell the contract before expiration and keep the profits.
In this example, both the futures buyer and seller hedge their risk. Company A needed oil in the future and wanted to offset the risk that the price may rise in December with a long position in an oil futures contract. The seller could be an oil company concerned about falling oil prices that wanted to eliminate that risk by selling or a futures contract that fixed the price it would get in December.
It is also possible that one or both of the parties are speculators with the opposite opinion about the direction of December oil. In that case, one might benefit from the contract, and one might not. Take, for example, the futures contract for West Texas Intermediate (WTI) oil that trades on the CME and represents 1,000 barrels of oil. If the price of oil rose from $62.22 to $80 per barrel, the trader with the long position—the buyer—in the futures contract would have profited $17,780 [($80 – $62.22) x 1,000 = $17,780].2 The trader with the short position—the seller—in the contract would have a loss of $17,780.
- Derivative trading is the purchase or sale of Derivatives in the share market.
- Trading in Derivatives revolves around the agreement between the trading parties to trade Derivatives in future for a predetermined price.
- Derivative trading usually happens according to the business hours of the share market.
What are the requirements for Derivatives trading?
While trading in Derivatives is similar to other kinds of trading, there are some requirements that traders must fulfil before they can begin trading in Derivatives:
- Traders are required to have an active demat account which is the account that stores securities in digital format.
- Traders must have a trading account through which the actual trade is conducted. The trading account is linked to the demat account and acts as the trader’s identity in the share market.
- Traders must deposit and maintain a fund which is a percentage of the total value of the underlying asset and the calculated price fluctuations. This process is called margin maintenance, and traders must do so daily as per price fluctuations.
Participants of Derivative Trading
Not all traders participate in the trade of Derivatives trading for the same reasons. Based on their goals, traders participating in Derivative trading can be broadly categorised into the following:
- Hedgers are risk-averse traders who trade in Derivatives to protect themselves from price fluctuations. They do so by fixing the price of an underlying asset and transferring risk associated with price fluctuations to risk-oriented speculators.
- Speculators are risk-oriented traders who take risks from Hedgers to profit from price fluctuations. They form an essential source of liquidity to the share markets.
- Arbitrageurs are low-risk traders who attempt to profit by selling the same asset for two different prices in two other markets.
Benefits of Derivative trading
Trading in Derivatives presents different benefits that can meet the needs of various investors:
- Trading in Derivatives involves lower transaction costs than in other forms of trading as the Derivatives act as risk management tools.
- Derivative trading can be a valuable tool for protection against price fluctuations as such fluctuations are already factored into contracts.
- Trading in Derivatives allows investors arbitrage opportunities to gain higher profits through speculations on price differences and fluctuations in different markets.
Drawbacks of Derivative Trading
While trading in Derivatives presents significant benefits to traders, they also have significant drawbacks which must be navigated for a successful trade:
- Derivatives are susceptible to price fluctuations, which can lead to severe loss if not managed properly.
- Contracts in Derivatives trading are challenging to break before expiration, which leaves traders vulnerable to market uncertainty.
- Trading in Derivatives requires extensive knowledge of complex processes of the financial markets, which makes it restrictive
What is the difference between futures and options contracts?
What are Derivatives? Derivatives Kya Hote Hai? Simple Explanation in Hindi Futures and options are two commonly known types of derivatives contracts. They derive their value from an underlying security, commodity, or index and the movements these assets make in the market.
However, futures and options contracts are different from one another. When you opt for a futures contract, you are obligated to buy or purchase an asset at a specific future date. On the other hand, when you opt for an options contract, you have the right but are not obligated, to buy or sell a specific asset at any given point during the contract term.
What is “margin money” in derivatives trading?
What are Derivatives? Derivatives Kya Hote Hai? Simple Explanation in Hindi Margin money in derivatives trading is the minimum amount a trader must deposit with the broker to enter into a derivatives contract. This amount is a specific percentage of the total value of the outstanding position. It acts as collateral and is used to cover any potential losses incurred during the trade.
What are the charges on derivatives contracts?
The charges that you might have to pay upon trading in derivatives contracts are as follows:
- Brokerage charges: Your broker will charge you for the services they provide that enable you to trade. The charges will vary as per the brokering house.
- Securities Transaction Tax (STT): The STT for futures is charged at 0.01% of the contract’s notional value. When it comes to options, the STT rate is 0.05% of the premium value. In both cases, STT is charged on the sell side, not the buy side.
- Exchange transaction charges: These are the charges payable to the stock exchange and are collected by the broker.
- Goods and Service Tax: This charge is levied on the brokerage amount and amounts to 18% of the brokerage and transaction charges.
- SEBI turnover fee: Charged by SEBI, it amounts to Rs 10 for every crore value of trade transacted.
- Stamp Duty: You also have to pay stamp duty as per standardised rates.
[contact-form][contact-field label=”Name” type=”name” required=”true” /][contact-field label=”Email” type=”email” required=”true” /][contact-field label=”Website” type=”url” /][contact-field label=”Message” type=”textarea” /][/contact-form]