What is Balance Sheet? Balance Sheet Kya Hota Hai? Simple Explanation in Hindi
What is Balance Sheet? Balance Sheet Kya Hota Hai? Simple Explanation in Hindi

Follow On Youtube :- @tradewithakanksha
What is Balance Sheet? Balance Sheet Kya Hota Hai? Simple Explanation in Hindi. A balance sheet is a financial statement that provides a snapshot of a company’s financial position at a specific point in time. It presents a summary of a company’s assets, liabilities, and shareholders’ equity. The balance sheet follows the fundamental accounting equation:
Assets = Liabilities + Shareholders’ Equity
Here’s a breakdown of the components of a balance sheet:
- Assets: These are the resources owned by the company that have economic value. Assets are typically categorized into two types:
- Current Assets: These are assets that are expected to be converted into cash or used up within one year or the operating cycle of the business. Examples include cash, accounts receivable (money owed by customers), inventory, and short-term investments.
- Non-Current Assets (or Long-Term Assets): These are assets that are expected to provide benefits over a longer period, usually beyond one year. Examples include property, plant, equipment, investments, and intangible assets (like patents or trademarks).
- Liabilities: These are the company’s obligations or debts to external parties. Liabilities are also categorized into two types:
- Current Liabilities: These are obligations that are expected to be settled within one year or the operating cycle. Examples include accounts payable (amounts owed to suppliers), short-term loans, and accrued expenses.
- Non-Current Liabilities (or Long-Term Liabilities): These are obligations that extend beyond one year. Examples include long-term loans, bonds payable, and deferred tax liabilities.
- Shareholders’ Equity (or Owner’s Equity): This represents the residual interest in the company’s assets after deducting its liabilities. It is the ownership claim on the company’s assets by its shareholders. Shareholders’ equity includes various components such as common stock, additional paid-in capital, retained earnings, and other comprehensive income.
What is Balance Sheet? Balance Sheet Kya Hota Hai? Simple Explanation in Hindi. The balance sheet is an important financial statement as it provides insights into a company’s financial health and its ability to meet its short-term and long-term obligations. It helps investors, creditors, analysts, and other stakeholders assess the company’s liquidity, solvency, and overall financial stability. Comparing balance sheets from different periods also enables the analysis of changes in a company’s financial position over time.
A cash flow statement is a financial statement that provides information about how cash and cash equivalents move in and out of a company during a specific period of time. It offers insights into a company’s ability to generate and utilize cash, which is crucial for its operational activities, investments, and financing.
What is Balance Sheet? Balance Sheet Kya Hota Hai? Simple Explanation in Hindi
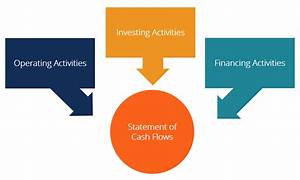
The cash flow statement is divided into three main sections:
- Operating Activities: This section reports the cash flows resulting from a company’s core operating activities, which involve the production and delivery of goods and services. It includes cash receipts from customers and cash payments to suppliers, employees, and other operating expenses. It also encompasses interest and dividend payments, income tax payments, and other cash flows directly tied to the company’s operations.
- Investing Activities: This section outlines the cash flows related to a company’s investment activities, which involve acquiring and disposing of long-term assets. It includes cash inflows from the sale of assets such as property, plant, equipment, and investments, as well as cash outflows for the purchase of those assets. Investing activities reflect a company’s capital expenditures and strategic decisions to acquire or sell assets.
- Financing Activities: This section details the cash flows related to a company’s financing activities, which involve raising capital and repaying obligations to creditors and shareholders. It includes cash inflows from issuing stocks, bonds, or loans and cash outflows from paying dividends, repurchasing company stock, and repaying debt.
What is Balance Sheet? Balance Sheet Kya Hota Hai? Simple Explanation in Hindi . At the end of each section, the net cash flow for that category is calculated by subtracting total cash outflows from total cash inflows. The three sections’ net cash flows are then summed to provide the overall change in cash and cash equivalents during the period. This change in cash is reconciled with the beginning and ending cash balances to ensure accuracy.
What is Balance Sheet? Balance Sheet Kya Hota Hai? Simple Explanation in Hindi The cash flow statement is a valuable tool for assessing a company’s liquidity, its ability to generate cash from its core operations, and its capacity to meet financial obligations and invest for future growth. By analyzing the components of the cash flow statement, investors and analysts can gain insights into a company’s financial health, cash management strategies, and its ability to withstand economic challenges. What is Balance Sheet? Balance Sheet Kya Hota Hai? Simple Explanation in Hindi
What is Balance Sheet? Balance Sheet Kya Hota Hai? Simple Explanation in Hindi A balance sheet is indeed a financial statement, and it’s one of the three primary financial statements used to provide a comprehensive view of a company’s financial health. The other two primary financial statements are the income statement (also known as the profit and loss statement) and the cash flow statement.
Here’s a brief explanation of each of these financial statements:
- Balance Sheet: As previously mentioned, the balance sheet provides a snapshot of a company’s financial position at a specific point in time. It presents a summary of a company’s assets, liabilities, and shareholders’ equity. The balance sheet follows the accounting equation: Assets = Liabilities + Shareholders’ Equity. It’s divided into current and non-current assets and liabilities and shows how a company’s resources (assets) are financed, whether through debt (liabilities) or equity (shareholders’ equity).
- Income Statement: The income statement, or profit and loss statement, reports a company’s financial performance over a specific period, typically a month, quarter, or year. It shows the revenues (sales, services, etc.) generated by the company and the expenses incurred in earning those revenues. The difference between revenues and expenses is the net income (profit) or net loss. The income statement provides a view of a company’s profitability during a specific time frame.
- Cash Flow Statement: The cash flow statement, as explained earlier, provides information about how cash and cash equivalents move in and out of a company during a specific period. It categorizes cash flows into operating, investing, and financing activities. It shows how a company generates and uses cash, which is essential for assessing its liquidity and cash management. What is Balance Sheet? Balance Sheet Kya Hota Hai? Simple Explanation in Hindi
Together, these financial statements provide a comprehensive view of a company’s financial performance, financial position, and cash management. They are essential tools for investors, creditors, analysts, and management to assess a company’s overall financial health and make informed decisions.
What is Balance Sheet? Balance Sheet Kya Hota Hai? Simple Explanation in Hindi A balance sheet represents the economic value of a company’s assets, liabilities, and shareholders’ equity at a specific point in time. Each of these components contributes to the economic value of the company in different ways:
- Assets: Assets represent the economic resources owned or controlled by the company. These resources have economic value because they can be used to generate future cash flows or provide other benefits. The economic value of assets can vary depending on their nature. For example, cash is highly liquid and can be easily converted into economic value, while long-term assets like machinery or real estate may have a more extended economic value over their useful life.
- Liabilities: Liabilities are the obligations or debts of the company. These represent amounts that the company owes to external parties. Liabilities also have economic value, as they represent claims on the company’s assets. The economic value of liabilities is typically the amount the company is obligated to repay or settle in the future.
- Shareholders’ Equity: Shareholders’ equity represents the residual interest in the assets of the company after deducting liabilities. It is the ownership claim on the company’s assets by its shareholders. The economic value of shareholders‘ equity represents the ownership stake’s value in the company, which can vary based on factors such as the company’s profitability and growth prospects.
The balance sheet’s primary purpose is to provide a snapshot of a company’s economic resources (assets) and the sources of financing (liabilities and equity) that have contributed to those resources at a specific point in time. The difference between total assets and total liabilities (known as shareholders’ equity or net assets) represents the economic value of the company to its shareholders.
It’s important to note that the economic value of a company can change over time due to various factors such as changes in asset values, fluctuations in liabilities, and shifts in market conditions. Investors, creditors, and other stakeholders use the balance sheet, along with other financial statements, to assess a company’s financial health and estimate its economic value .What is Balance Sheet? Balance Sheet Kya Hota Hai? Simple Explanation in Hindi
- Current Liabilities: Loans that are expected to be repaid within one year or the operating cycle of the business (whichever is longer) are classified as current liabilities. These are short-term loans, and their balance decreases as the company makes payments on them. Current liabilities also include other short-term obligations such as accounts payable and accrued expenses.
- Non-Current Liabilities (or Long-Term Liabilities): Loans that have a repayment schedule extending beyond one year are classified as non-current liabilities. These are long-term loans, and their balance may be due over several years. Non-current liabilities also include other long-term obligations like bonds payable.
Here’s a simplified example of how a loan might appear on a balance sheet:
Balance Sheet
As of [Specific Date]
Assets:
- Current Assets
(List current assets here)
- Non-Current Assets
(List non-current assets here)
Liabilities:
- Current Liabilities
- Accounts Payable
- Accrued Expenses
- Short-Term Loan 1 $XX,XXX
- Short-Term Loan 2 $XX,XXX
(List other current liabilities here)
- Non-Current Liabilities
- Long-Term Loan 1 $XX,XXX
- Long-Term Loan 2 $XX,XXX
(List other non-current liabilities here)
Shareholders' Equity:
(List components of shareholders' equity here)
In this example, you can see that the loans are listed under both current and non-current liabilities based on their repayment timelines. As payments are made on these loans, the balances will decrease, and the reduction will be reflected on the balance sheet. It’s important for investors and stakeholders to analyze the balance sheet to understand the company’s debt obligations and its ability to manage and service those loans. What is Balance Sheet? Balance Sheet Kya Hota Hai? Simple Explanation in Hindi
Owner’s equity, also known as shareholders’ equity or stockholders’ equity, represents the residual interest in a company’s assets after deducting its liabilities. In simpler terms, it’s the net value of the company’s assets that belong to its owners or shareholders. Owner’s equity is a critical component of a company’s balance sheet, and it reflects the ownership stake in the business .What is Balance Sheet? Balance Sheet Kya Hota Hai? Simple Explanation in Hindi
Here’s how owner’s equity is calculated and understood:
Owner’s Equity = Total Assets – Total Liabilities
- Total Assets: This is the sum of all the economic resources owned by the company. Assets can include cash, accounts receivable, inventory, property, equipment, investments, and more. These assets represent what the company owns.
- Total Liabilities: These are the company’s obligations and debts. They include items like accounts payable, loans, bonds, and other liabilities that represent what the company owes to external parties.
Owner’s equity is essentially the “net worth” or “book value” of the company from the perspective of its shareholders. If a company were to sell all its assets and pay off all its liabilities, the remaining amount would be the owner’s equity. In a real-world context, owner’s equity represents the shareholders’ claim on the assets of the company. It’s what the shareholders would collectively receive if the company were to be liquidated.
Owner’s equity can change over time due to several factors:
- Profit or Loss: Net income or net loss from the income statement is typically added to or subtracted from owner’s equity. If a company generates a profit, it increases owner’s equity, and if it incurs a loss, it decreases owner’s equity.
- Share Issuances and Repurchases: The issuance of new shares or the repurchase of existing shares can impact owner’s equity.
- Dividends: When a company pays dividends to its shareholders, it reduces owner’s equity.
What is Balance Sheet? Balance Sheet Kya Hota Hai? Simple Explanation in Hindi Owner’s equity is important for investors and analysts because it provides insights into the financial health and value of the company from the shareholders’ perspective. It’s an essential metric for evaluating a company’s financial stability and assessing its ability to generate value for its owners.

The term “balance sheet” is derived from the fundamental accounting equation, which is:
Assets = Liabilities + Shareholders’ Equity
This equation must always “balance,” meaning that the total value of assets must be equal to the total value of liabilities and shareholders’ equity. This principle of balance is at the core of the accounting system.
The balance sheet is so named because it provides a snapshot of a company’s financial position at a specific point in time, What is Balance Sheet? Balance Sheet Kya Hota Hai? Simple Explanation in Hindi with assets on one side and liabilities and shareholders’ equity on the other side. The equality of the two sides demonstrates that the company’s resources (assets) are financed either by borrowing money (liabilities) or by the owners’ investments (shareholders’ equity).
In essence, the balance sheet shows that a company’s assets are balanced or matched by its sources of funds (liabilities and equity). If the balance sheet doesn’t balance, it indicates an error in the accounting records, which needs to be corrected before the financial statements can be considered accurate.
So, the term “balance sheet” reflects its purpose of providing a balanced view of a company’s financial position by showing how its assets are funded. What is Balance Sheet? Balance Sheet Kya Hota Hai? Simple Explanation in Hindi It’s a fundamental financial statement used for assessing a company’s financial health and stability.
Creating a balance sheet involves several steps and methods to accurately present a company’s financial position at a specific point in time. Here’s a general outline of the process:
- Gather Financial Data:
- Collect all relevant financial data, including the values of all assets, liabilities, and shareholders’ equity components as of the reporting date. This data can be sourced from a company’s accounting records, financial statements, and supporting documentation.
- Classify Assets and Liabilities:
- Classify assets and liabilities into current and non-current (long-term) categories. Current assets and liabilities are those expected to be realized or settled within one year or the operating cycle of the business, while non-current assets and liabilities extend beyond that timeframe.
- List Assets:
- Start the balance sheet by listing all assets. Common asset categories include:
- Current Assets (e.g., cash, accounts receivable, inventory)
- Non-Current Assets (e.g., property, plant, equipment, investments)
- Start the balance sheet by listing all assets. Common asset categories include:
- List Liabilities:
- After listing assets, list all liabilities. Common liability categories include:
- Current Liabilities (e.g., accounts payable, short-term loans)
- Non-Current Liabilities (e.g., long-term loans, bonds payable)
- After listing assets, list all liabilities. Common liability categories include:
- Calculate Owner’s Equity:
- Calculate owner’s equity by subtracting total liabilities from total assets. What is Balance Sheet? Balance Sheet Kya Hota Hai? Simple Explanation in Hindi The owner’s equity section also includes additional details such as retained earnings and other comprehensive income.
- Ensure the Equation Balances:
- Confirm that the accounting equation (Assets = Liabilities + Owner’s Equity) balances. The total assets should equal the total liabilities and owner’s equity. If they don’t match, there may be errors in the data or calculations that need to be corrected.
- Present the Balance Sheet:
- Organize the information in a standard format, with assets on the left-hand side and liabilities and owner’s equity on the right-hand side. Typically, assets are listed in order of liquidity, What is Balance Sheet? Balance Sheet Kya Hota Hai? Simple Explanation in Hindi with current assets presented before non-current assets. Liabilities are similarly presented with current liabilities first, followed by non-current liabilities.
- Provide Notes and Disclosures:
- Include any necessary notes and disclosures to provide additional context or explanations for specific items on the balance sheet. These notes can help readers understand the company’s financial position better.
- Review and Audit:
- Conduct a thorough review of the balance sheet to ensure accuracy. Many companies also have their financial statements audited by external auditors for an independent verification of their accuracy and compliance with accounting standards.
- Distribution:
- The balance sheet, along with other financial statements, is typically distributed to shareholders, potential investors, lenders, and regulatory authorities as required by law.
What is Balance Sheet? Balance Sheet Kya Hota Hai? Simple Explanation in Hindi . It’s important to note that creating a balance sheet follows generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP) or the applicable accounting standards in the region or country where the company operates. These principles govern how financial information is recorded, presented, and disclosed to ensure consistency and transparency in financial reporting. Additionally, the format and content of a balance sheet can vary depending on the industry and specific reporting requirements.
An annual report typically includes a balance sheet as one of its key financial statements. The balance sheet, also known as the statement of financial position, provides a snapshot of a company’s financial condition at a specific point in time, usually at the end of the fiscal year. It is one of the three main financial statements in an annual report, alongside the income statement and cash flow statement.
Here’s an overview of what you might find in a balance sheet within an annual report:
- Assets: The balance sheet begins with a list of the company’s assets, which are categorized into two main types:
a. Current Assets: These are assets that are expected to be converted into cash or used up within one year. Common current assets include cash, accounts receivable, inventory, and short-term investments.
b. Non-Current Assets (or Long-Term Assets): These are assets that are not expected to be converted into cash within one year. Non-current assets include property, plant, equipment, investments in subsidiaries or affiliates, and intangible assets like patents and trademarks.
- Liabilities: The second section of the balance sheet lists the company’s liabilities. Similar to assets, liabilities are divided into two categories:
a. Current Liabilities: These are obligations that are expected to be settled within one year. Common current liabilities include accounts payable, short-term loans, and accrued expenses.
b. Non-Current Liabilities (or Long-Term Liabilities): These are obligations that are not expected to be settled within one year. Examples include long-term loans, bonds payable, and deferred tax liabilities.
- Equity: The final section of the balance sheet shows the company’s equity, which represents the residual interest in the assets of the entity after deducting liabilities. It includes common stock, retained earnings, and other comprehensive income. Equity is essentially the ownership stake held by shareholders.
The balance sheet follows the basic accounting equation:
This equation must always balance. In other words, the total value of assets must equal the total of liabilities and equity.
The balance sheet provides important information about a company’s financial health and its ability to meet its short-term and long-term obligations. What is Balance Sheet? Balance Sheet Kya Hota Hai? Simple Explanation in Hindi Investors, creditors, and other stakeholders use the balance sheet to assess the company’s liquidity, solvency, and overall financial stability.
In an annual report, the balance sheet is usually accompanied by notes and disclosures that provide additional details about the company’s accounting policies, valuation methods, and any contingencies or commitments that may affect the financial position. These notes are essential for understanding the context behind the numbers presented in the balance sheet.
In a balance sheet, equity share capital and retained earnings are both components of the equity section. Let’s break down what each of these items represents:
What is Balance Sheet? Balance Sheet Kya Hota Hai? Simple Explanation in Hindi
- Equity Share Capital:
- Equity share capital, also known as common stock or share capital, represents the ownership interest of the shareholders in the company.
- It is the total value of shares issued by the company to its shareholders in exchange for ownership stakes.
- Equity share capital is typically recorded at the par value or nominal value of the shares, although in some cases, it may be recorded at the issue price.
- This value represents the initial investment made by shareholders in the company.
- Retained Earnings:
- Retained earnings are the accumulated profits or losses of the company that have been retained and reinvested into the business over time.
- It represents the portion of the company’s net income that has not been distributed to shareholders in the form of dividends.
- Retained earnings can be positive, indicating that the company has accumulated profits over time, or negative (accumulated losses), indicating that the company has sustained losses over time.
- It is an important indicator of the company’s historical financial performance and its ability to generate profits.
In a balance sheet, these two components are typically presented in the equity section as follows:
- This section includes the par value or nominal value of the shares issued by the company. It represents the initial investments made by shareholders.
- The value of equity share capital is usually presented under the “Shareholders’ Equity” or “Owner’s Equity” heading.
- Retained earnings are typically presented under the “Retained Earnings” or “Accumulated Deficit” heading in the equity section.
- This value reflects the cumulative profits earned by the company minus any cumulative losses and dividends paid to shareholders.
Here’s a simplified representation of the equity section in a balance sheet:
Shareholders' Equity
Equity Share Capital $X
Retained Earnings $Y
Total Equity $ZIn this representation, the total equity is the sum of the equity share capital and retained earnings. It represents the shareholders’ total interest in the company’s assets after deducting its liabilities.
It’s important to note that the equity section of the balance sheet provides insights into the company’s financial structure and the ownership interests of shareholders. It also shows how much of the company’s profits have been reinvested to support its growth and operations over time.
Creating a balance sheet involves listing a company’s assets, liabilities, and equity at a specific point in time. Below is a simplified example of a balance sheet format:
Balance Sheet
As of [Date]
---------------------------------------------------------------
ASSETS
---------------------------------------------------------------
Current Assets:
- Cash and Cash Equivalents $X
- Accounts Receivable $Y
- Inventory $Z
- Other Current Assets $W
Total Current Assets $Total_Current_Assets
Non-Current Assets:
- Property, Plant, and Equipment $A
- Intangible Assets $B
- Investments $C
- Other Non-Current Assets $D
Total Non-Current Assets $Total_Non_Current_Assets
Total Assets $Total_Assets
---------------------------------------------------------------
LIABILITIES
---------------------------------------------------------------
Current Liabilities:
- Accounts Payable $P
- Short-Term Loans $Q
- Accrued Expenses $R
- Other Current Liabilities $S
Total Current Liabilities $Total_Current_Liabilities
Non-Current Liabilities:
- Long-Term Loans $L
- Bonds Payable $M
- Other Non-Current Liabilities $N
Total Non-Current Liabilities $Total_Non_Current_Liabilities
Total Liabilities $Total_Liabilities
---------------------------------------------------------------
EQUITY
---------------------------------------------------------------
- Equity Share Capital $E
- Retained Earnings $F
- Other Equity Items $G
Total Equity $Total_Equity
---------------------------------------------------------------
Total Liabilities and Equity $Total_Liabilities_Equity
Here’s a step-by-step explanation of each section:
- ASSETS:
- List all the company’s assets, starting with current assets (those expected to be converted to cash or used within one year) and followed by non-current assets (those with a longer lifespan).
- Total Assets:
- Calculate the total value of all assets by adding up the current and non-current assets.
- LIABILITIES:
- List all the company’s liabilities, beginning with current liabilities (obligations expected to be settled within one year) and followed by non-current liabilities (obligations with a longer-term maturity).
- Total Liabilities:
- Calculate the total value of all liabilities by adding up the current and non-current liabilities.
- EQUITY:
- List equity components, which typically include equity share capital, retained earnings, and other equity items if applicable.
- Total Equity:
- Calculate the total equity by adding up all the equity components.
- Total Liabilities and Equity:
- This line represents the sum of total liabilities and total equity and must equal the total value of assets. This demonstrates that the accounting equation (Assets = Liabilities + Equity) is balanced.
What is Balance Sheet? Balance Sheet Kya Hota Hai? Simple Explanation in Hindi Ensure that the values entered in the balance sheet are accurate and represent the financial position of the company as of the specified date. Keep in mind that a balance sheet is a snapshot at a specific moment and may change over time as transactions occur.
[contact-form][contact-field label=”Name” type=”name” required=”true” /][contact-field label=”Email” type=”email” required=”true” /][contact-field label=”Website” type=”url” /][contact-field label=”Message” type=”textarea” /][/contact-form]
What is Balance Sheet? Balance Sheet Kya Hota Hai? Simple Explanation in Hindi A balance sheet is one of the three main financial statements used in accounting and financial reporting, with the other two being the income statement and the cash flow statement. The balance sheet provides a snapshot of a company’s financial position at a specific point in time, typically at the end of a fiscal period, such as a quarter or a year. It’s called a “balance sheet” because it adheres to the fundamental accounting equation:
Here’s an explanation of the key components of a balance sheet:
- Assets:
- Assets represent everything that a company owns or controls that has economic value. What is Balance Sheet? Balance Sheet Kya Hota Hai? Simple Explanation in Hindi Assets are divided into two main categories:
a. Current Assets: These are assets that are expected to be converted into cash or used up within one year or one operating cycle (whichever is longer). Common current assets include cash, accounts receivable (money owed to the company by customers), inventory (goods ready for sale), and short-term investments.
b. Non-Current Assets (or Long-Term Assets): These are assets that are not expected to be converted into cash within one year. What is Balance Sheet? Balance Sheet Kya Hota Hai? Simple Explanation in Hindi They include property, plant, and equipment (physical assets like buildings and machinery), intangible assets (such as patents and trademarks), long-term investments, and other assets like goodwill.
- Liabilities:
- Liabilities represent the company’s obligations or debts. They are also divided into two main categories:
a. Current Liabilities: These are obligations that are expected to be settled within one year or one operating cycle (whichever is longer). Common current liabilities include accounts payable (money owed to suppliers), short-term loans, accrued expenses, and other short-term debts.
b. Non-Current Liabilities (or Long-Term Liabilities): These are obligations that are not expected to be settled within one year. Examples include long-term loans, bonds payable, deferred tax liabilities, and other long-term debts.
- Equity:
- Equity represents the residual interest in the assets of the entity after deducting liabilities. What is Balance Sheet? Balance Sheet Kya Hota Hai? Simple Explanation in Hindi In other words, it’s the ownership interest in the company. Equity includes:
a. Equity Share Capital (or Common Stock): This is the amount of capital invested by shareholders when they purchase shares in the company.
b. Retained Earnings: This is the cumulative net income (profits) earned by the company over time, minus any dividends paid to shareholders. It reflects the portion of profits that the company has retained and reinvested into the business.
c. Other Comprehensive Income: This includes gains or losses that bypass the income statement but affect equity, such as changes in the value of certain investments.
The balance sheet equation (Assets = Liabilities + Equity) must always balance. What is Balance Sheet? Balance Sheet Kya Hota Hai? Simple Explanation in Hindi This means that the total value of assets must equal the total of liabilities and equity. This principle is fundamental to double-entry accounting, which is the basis for accurate financial record-keeping.
What is Balance Sheet? Balance Sheet Kya Hota Hai? Simple Explanation in Hindi The balance sheet is a critical financial statement that provides valuable insights into a company’s financial health, liquidity, solvency, and overall financial condition. It is an essential tool for investors, creditors, management, and other stakeholders when assessing a company’s financial position. What is Balance Sheet? Balance Sheet Kya Hota Hai? Simple Explanation in Hindi
