We’ll delve into the investment minds of Warren Buffett and Charlie Munger as we explore their profound perspectives on the high returns of capital. We’ll try to gain insights by looking into their perspective on capital deployment by companies. As an investor, we know that a company that can yield high returns of capital will be preferred over others.
In stock investing, the pursuit of a high return on capital (ROC) should be the target for every savvy investor. The notion of efficiently deploying capital to yield substantial gains has long been a cornerstone of successful wealth-building strategies. Let’s delve into the profound wisdom of two legendary investment maestros: Warren Buffett and Charlie Munger. Their distinguished approaches to capital deployment offer invaluable insights that transcend the realms of finance.
Warren Buffett and Charlie Munger have a profound ability to identify promising investments and nurture them into financial powerhouses. The core of their philosophy is the concept of high returns on capital. Here there is an interplay between capital infusion and future returns (growth of capital). This is the essence of compounding.
As we navigate the terrain of these investment virtuosos, we uncover the dual facets of their strategies. Buffett’s aspiration for businesses capable of compounding capital at remarkable rates is juxtaposed with Munger’s inclination towards enterprises requiring minimal capital yet yielding exceptional returns. These two perspectives intertwine, illustrating the nuanced approaches that underpin their successes.
Through a lens tinted with pragmatism, we will dissect the practicality of realizing the ideal business – a phenomenon characterized by sustained high returns and a voracious appetite for capital reinvestment. While such entities may appear rare, the investment philosophies of Buffett and Munger prove adaptable to the intricate tapestry of real-world scenarios.
Join us as we unravel the strategies employed by these luminaries, unlocking the door to achieving ‘High Returns of Capital’ in a realm of financial opportunity.
In the intricate realm of investment, the art of capital deployment stands as a pivotal determinant of financial success. Effectively channeling resources into ventures that yield substantial returns is a hallmark of astute investors. Warren Buffett and Charlie Munger, have each crafted unique strategies when it comes to capital deployment, adding depth and dimension to the pursuit of ‘High Returns of Capital’.
Capital deployment is not merely a matter of investing resources; it is a strategy that can either amplify or constrain potential gains. The ability to allocate funds judiciously is key to generating returns that outpace the initial investment. This concept underscores the significance of capital deployment strategies – a facet that both Buffett and Munger have embraced with distinct perspectives.
Warren Buffett, renowned as one of the most successful investors of our time, places a premium on businesses with the potential to compound capital at extraordinary rates. This approach hinges on the power of compounding – the ability of an investment to generate earnings that are subsequently reinvested, resulting in exponential growth over time.
Businesses with this capability become compounding machines, transforming capital injections into a self-perpetuating cycle of wealth creation.
In contrast, Charlie Munger emphasizes a different aspect of capital deployment. Munger is drawn to businesses that demand minimal additional capital while delivering outsized returns.
This philosophy is rooted in the principle of efficiency – by requiring less capital for growth, a business can achieve substantial returns without the need for extensive reinvestment.
These divergent yet complementary strategies illuminate the multifaceted nature of capital deployment. While Buffett’s approach harnesses the power of sustained compounding, Munger’s perspective capitalizes on resource-efficient enterprises.
Within the realm of investment philosophy, few concepts hold as much allure as the notion of the “ideal business” – a formidable entity capable of generating high returns on capital while seamlessly reinvesting significant resources at those same compelling rates.
This visionary approach championed by Warren Buffett transcends mere investment strategies, encapsulating the essence of compounding wealth through capital deployment.
Buffett’s concept of the ideal business mirrors a perpetual motion engine, harnessing the twin forces of impressive returns and judicious capital reinvestment.
In this financial alchemy, every dollar invested becomes a catalyst for future growth, setting in motion a self-sustaining cycle of compounded returns. Such a business transforms capital into a dynamic force that propels it forward, consistently outperforming conventional investment models.
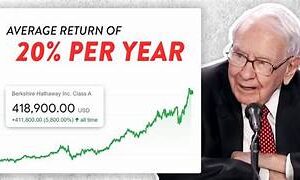
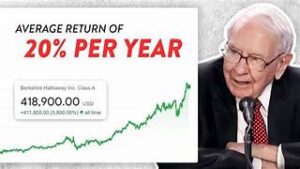
Consider the quintessential example of Berkshire Hathaway itself – an ideal business. Over the decades, Buffett nurtured Berkshire Hathaway into a compounding machine, a financial juggernaut that continually reinvests capital into diverse ventures, generating remarkable returns. Each subsidiary, operating with operational autonomy and contributing to the parent company’s bottom line, exemplifies the principle of capital compounding in action.
The idea of the ideal business goes beyond profit. It embodies a strategic vision where capital’s ability to generate returns becomes a driving force for success. By understanding and applying Buffett’s principles of capital deployment, investors can uncover opportunities that embody the essence of a compounding machine.
While the concept of businesses capable of deploying increasing capital at consistently high rates of return evokes intrigue and aspiration, a reality check reveals their rarity within the investment landscape. Warren Buffett’s pursuit of the ideal business, a compounding machine capable of exponential growth through capital deployment, is indeed a formidable vision. Yet, the real world often demonstrates that such entities are few and far between.
Enterprises like Coca-Cola and See’s Candy stand as testaments to the distinct dichotomy between impressive returns and incremental capital deployment. These big brands, while undoubtedly possessing the capacity to generate handsome profits, deviate from the paradigm of unceasing capital compounding. Their hallmark lies in the art of generating substantial returns without necessitating substantial injections of additional capital.
Coca-Cola, an emblem of global consumerism, thrives on its brand strength and distribution network, attributes that enable it to churn out considerable profits with very low capital requirements. Similarly, See’s Candy, renowned for its delectable confections, exemplifies the power of consistent returns achieved without perpetual capital reinvestment.
While these companies have certainly achieved remarkable financial success, the “relentless compounding of capital” is not a defining characteristic of their business models.
This reality underscores the rarity of businesses that fit the mold of the ideal compounding machine described by Warren Buffett.
While the pursuit of such entities remains a cornerstone of investment aspiration, it is imperative to acknowledge the paucity of these opportunities in practice.
In the orchestration of capital deployment strategies, the structure of an investment conglomerate assumes a pivotal role in amplifying returns and optimizing resources. Warren Buffett’s Berkshire Hathaway stands as an exemplar of this strategic ingenuity. It is an example of the art of reallocating capital across diverse businesses.
At the heart of Berkshire Hathaway’s design lies a flexibility that allows for agile capital reallocation. This distinctive structure enables the conglomerate to harness the advantages of moving cash fluidly across its array of subsidiaries and ventures. This capability often likened to a financial chessboard, grants Buffett and his team the power to strategically position resources where they are best poised to generate substantial returns.
The art of reallocating capital within Berkshire Hathaway is a symphony of precision. Cash generated by one subsidiary’s success can be seamlessly channeled into another. This way they are maximizing the potential for growth and compounding returns. This dynamic movement allows the conglomerate to transcend the limitations that often constrain businesses with “restricted capital deployment opportunities.”
The advantages of this structure are manifold. It affords Berkshire Hathaway the ability to capitalize on opportunities that emerge across a diverse spectrum of industries, mitigating risk and capitalizing on emerging trends. The conglomerate’s unparalleled flexibility in reallocating capital underscores the essence of a compounding machine, an attribute that echoes Buffett’s visionary concept of an ideal business.
Industry characteristics emerge as a fundamental determinant in the effectiveness of capital deployment. Industries with rapidly evolving landscapes, such as technology, demand nimble resource allocation to capitalize on opportunity.
Conversely, more stable sectors may warrant longer-term capital strategies for sustained growth. The dynamics of each industry shape the tempo at which capital is infused and returns are realized.
Growth opportunities act as catalysts for capital deployment. Businesses poised for expansion necessitate significant resource allocation to seize untapped potential. These opportunities may manifest as market expansions, technological innovation, or strategic acquisitions. The ability to accurately assess growth prospects and allocate resources accordingly is pivotal in achieving high returns on capital.
A company’s internal financial health and management efficacy also play a pivotal role. Prudent capital deployment hinges on adept management, capable of identifying avenues for strategic resource allocation. A company’s track record of capital utilization and its ability to generate returns are indicators of its potential to amplify capital effectiveness.
Furthermore, external economic conditions and market volatility influence the viability of capital deployment strategies. Economic shifts may necessitate agility in reallocating resources to mitigate risks and capitalize on emerging trends. Adaptability to these external forces is a hallmark of successful capital deployment.
There are two types of great businesses we’ll see in the market. A few are ones that are bearing surplus cashand those exhibiting good returns yet constrained reinvestment opportunities.
As an investor, we must learn to deal with these types of companies differently. These distinct businesses demand distinct strategies, each harboring its own set of challenges and advantages.
- Enterprises with surplus cash stand as a testament to financial prowess. They generate robust profits that exceed operating expenses, resulting in surplus funds. It leads to cash abundance. This cash grants flexibility, allowing businesses to explore expansion, diversification, or strategic acquisitions. Such companies can seize opportunities swiftly. They can use the available resources for strategic growth. However, the surplus cash must be efficiently managed. The decision-making of the top management on how to deploy this cash must yield substantial returns. The challenge lies in identifying ventures that align with the business’s core competencies and amplify shareholder value.
- Businesses that report high returns but possess limited reinvestment avenues tread a more complex path. These enterprises excel in generating profits, yet their capital requirements for growth may be modest. Such businesses may lack the potential to magnify returns through substantial capital infusion. The advantage here lies in stability; they can channel profits into dividends. This way they can reward shareholders while sustaining the core business. However, the challenge surfaces when they want to see fast growth. As they have limited opportunities for reinvestment, it can lead to stagnation.
A judicious blend of surplus cash utilization and focused reinvestment is the compass. By adeptly navigating the duality presented by these contrasting business types, investors can harmonize returns, growth, and stability, inching closer to the elusive realm of ‘High Returns of Capital’.
In the realm of investment, the ideals of capital compounding may appear ethereal, reserved for the rarefied few who discover businesses capable of perpetual reinvestment at high rates of return.
However, the seasoned wisdom of Warren Buffett and Charlie Munger reveals a pragmatic reality: while true compounding machines are a rarity, there’s immense value in businesses that consistently generate good returns on capital.
Buffett and Munger, despite their reverence for the elusive ‘ideal business’, pragmatically navigate the investment landscape by embracing opportunities that exhibit commendable returns. Their investment philosophies pivot on recognizing the power of sustained profitability. They also acknowledge that there are very less businesses around that can deploy vast capital at high rates of return.
In practice, these investment maestros identify businesses that display the potential for steady returns and judicious capital utilization. Such enterprises may not be a compounding machine, yet they display the characteristics of sustainability and consistency of earnings.
Such companies should become integral components of our stock portfolios. They will act as pillars of stability in an unpredictable financial terrain.
In stock investing, the pursuit of High Returns of Capital finds its anchor in the strategic artistry of Warren Buffett and Charlie Munger. While the ideal compounding machine remains a rarity, their wisdom illuminates a multifaceted approach.
Embracing businesses that deliver steady returns and leveraging flexible capital deployment within Berkshire Hathaway’s canvas, they forge a path where realism harmonizes with aspiration.
As investors navigate the landscape, the resounding lesson is clear: while compounding may be elusive, “judicious capital utilization” and “sustained profitability” remain within reach. These two objectives in stock investing are a timeless strategy for financial success.
[contact-form][contact-field label=”Name” type=”name” required=”true” /][contact-field label=”Email” type=”email” required=”true” /][contact-field label=”Website” type=”url” /][contact-field label=”Message” type=”textarea” /][/contact-form]




![Advantages And Disadvantages Of Artificial Intelligence [AI]](https://tradewithakanksha.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/12/the-power-of-AI-1024x585.jpg)