-
Virat Kohli is an Indian cricketer is Best 20 BatsMen in Cricket widely regarded as one of the greatest batsmen of his generation. He was born on November 5, 1988, in Delhi, India. Kohli is known for his exceptional batting skills, consistency, and aggressive playing style. He has achieved numerous records and accolades throughout his cricket career.here are some highlights of Virat Kohli’s cricketing achievements: 
- Captaincy: Virat Kohli has been the captain of the Indian cricket team in various formats, including Test matches and One Day Internationals (ODIs). Under his leadership, the Indian team achieved significant successes.
- Batting Records: Kohli has consistently performed at a high level across all formats of the game. He holds numerous batting records, including being one of the fastest players to score thousands of runs in ODIs and Tests.
- ODI Cricket: He has been among the top run-scorers in ODIs, with numerous centuries to his name. He held the record for the fastest century in ODIs at the time.
- Test Cricket: Kohli’s performance in Test cricket has also been exceptional. He has scored numerous centuries and has been a key player in India’s Test victories both at home and abroad.
- ICC Tournaments: He has performed well in various ICC tournaments, including the ICC Cricket World Cup and ICC T20 World Cup.
- Consistency: One of Kohli’s notable qualities is his remarkable consistency across different formats and conditions.
- Awards and Recognition: He has received several awards, including the prestigious Sir Garfield Sobers Trophy for ICC Cricketer of the Year multiple times.
- Fitness and Work Ethic: Kohli is known for his dedication to fitness and training, which has contributed to his on-field success.
Steve Smith is an Australian cricketer known for his exceptional batting skills and unorthodox playing style in Best 20 BatsMen in Cricket. He was born on June 2, 1989, in Sydney, Australia. Smith is widely considered one of the best Test batsmen in the world and has achieved numerous records and accolades throughout his cricket career.here are some highlights of Steve Smith’s cricketing achievements:
- Test Cricket Excellence: Smith is particularly renowned for his performances in Test cricket. He has a unique batting technique and an incredible ability to read bowlers, which has contributed to his high success rate.
- Batting Records: He has consistently been among the top run-scorers in Test cricket. He held the number one ranking in the ICC Test Batting Rankings for an extended period.
- Ashes Dominance: Smith has been a standout performer in the Ashes series between Australia and England. His performances in these series have been crucial in Australia’s success.
- Consistency: Smith’s consistency in Test cricket is remarkable, with a high number of centuries and a strong average.
- Captaincy: Smith has also captained the Australian cricket team. However, his captaincy was temporarily suspended due to his involvement in the ball-tampering scandal in 2018.
- Comeback after Suspension: After serving a one-year suspension for his role in the ball-tampering incident, Smith made a successful comeback to international cricket and continued to excel with the bat.
- Unconventional Style: Smith’s batting technique is often described as unorthodox but highly effective. He has a unique trigger movement before facing deliveries, which adds to the challenge for bowlers.
- ODI and T20 Cricket: While Smith’s main strength lies in Test cricket, he has also played in One Day Internationals (ODIs) and T20 Internationals for Australia
Kane Williamson is a New Zealand cricketer who is widely regarded as one of the best batsmen in the world and an exceptional leader. He was born on August 8, 1990, in Tauranga, New Zealand. Williamson is known for his elegant batting style, impeccable technique, and calm demeanor on and off the field. here are some highlights of Kane Williamson’s cricketing achievements:
- Captaincy: Williamson has been the captain of the New Zealand cricket team in all formats. He is highly regarded for his leadership skills and ability to foster a positive team environment.
- Batting Prowess: Williamson is known for his consistent performances across formats, particularly in Test cricket. He has a solid technique that allows him to succeed on a variety of pitches.
- Test Cricket Excellence: He has been a key player in New Zealand’s Test cricket successes. He has led the team to significant victories and has also been a pillar of strength in challenging conditions.
- 2019 ICC Cricket World Cup: Under Williamson’s captaincy, New Zealand reached the final of the ICC Cricket World Cup in 2019. The final match ended in a tie, and England won on the boundary countback rule.
- ODI and T20 Cricket: While his main strength is in Test cricket, Williamson has also been successful in One Day Internationals (ODIs) and T20 Internationals. He is known for his adaptability across formats.
- Gentlemanly Demeanor: Williamson is often praised for his sportsmanship, humility, and fair play. He is respected by fellow players and fans alike for his conduct on and off the field.
- Records and Achievements: Williamson has numerous records and achievements to his name, including being one of New Zealand’s all-time leading run-scorers in international cricket.
- Consistency: His ability to consistently score runs and lead by example has made him a highly regarded figure in the cricketing world.
Kane Williamson’s career and accomplishments may have evolved since then. For the most current and accurate information about his career, I recommend checking official cricket sources or news outlets.
Joe Root is an English cricketer who is known for his elegant batting style, technical prowess, and leadership skills. He was born on December 30, 1990, in Sheffield, England. Root is considered one of the leading batsmen in the world and has been a key player for the England cricket team. here are some highlights of Joe Root’s cricketing achievements:
- Captaincy: Root has served as the captain of the England cricket team in Test matches since 2017. Under his leadership, England has achieved notable successes, including series victories against strong teams.
- Batting Excellence: He is known for his classical batting technique and ability to adapt to different formats and conditions. Root has been a consistent run-scorer for England in all formats of the game.
- Test Cricket Prowess: Root’s performance in Test cricket has been particularly noteworthy. He has scored numerous centuries and is one of England’s top run-scorers in the format.
- Ashes Series: Root has been a significant performer in the Ashes series against Australia. His performances against Australia’s strong bowling attack have been crucial for England’s chances.
- ODI and T20 Cricket: While he has mainly been associated with Test cricket, Root has also been part of England’s One Day Internationals (ODIs) and T20 Internationals squads. He is known for his ability to anchor an innings in ODIs.
- Records and Achievements: Root has broken several records and achieved various milestones during his career. He is often regarded as one of the best English batsmen of his generation.
- Leadership Qualities: Root’s leadership qualities, both on and off the field, have earned him respect from teammates and opponents alike.
- Consistency: His ability to consistently perform and provide stability to the England batting lineup has been a key asset for the team.
Joe Root’s career and accomplishments may have evolved since then. For the most current and accurate information about his career, I recommend checking official cricket sources or news outlets.
Rohit Sharma is an Indian cricketer known for his explosive batting style and ability to score big runs. He was born on April 30, 1987, in Bansod, Nagpur, India. Rohit is considered one of the most talented and successful limited-overs batsmen in the world. here are some highlights of Rohit Sharma’s cricketing achievements:

- Limited-Overs Dominance: Rohit is particularly renowned for his performances in limited-overs cricket, especially One Day Internationals (ODIs) and Twenty20 Internationals (T20Is). He has been an integral part of India’s white-ball cricket success.
- Opening Batsman: Rohit is known for his role as an opening batsman in limited-overs cricket. He has been highly successful in providing solid starts to the Indian team.
- Double Centuries in ODIs: Rohit is the only cricketer to have scored three double centuries in ODIs. He holds the record for the highest individual score in ODIs, with 264 runs.
- T20 Records: He has also excelled in T20 cricket, both for the Indian national team and in domestic leagues like the Indian Premier League (IPL).
- IPL Success: Rohit Sharma is the captain of the Mumbai Indians in the IPL. Under his leadership, the team has won multiple IPL championships.
- Vice-Captaincy: Rohit has served as the vice-captain of the Indian cricket team in various formats. He has provided valuable leadership support to the team.
- Big Match Performer: Rohit has a reputation for delivering strong performances in crucial matches and tournaments.
- Batting Style: His batting style combines elegant strokeplay with the ability to hit big shots, making him a dynamic and entertaining player to watch.
- Records and Achievements: Rohit has numerous records and achievements to his name, including being one of the leading run-scorers for India in limited-overs cricket.
Rohit Sharma’s career and accomplishments may have evolved since then. For the most current and accurate information about his career, I recommend checking official cricket sources or news outlets.
Babar Azam is a Pakistani cricketer who is known for his stylish batting, consistency, and leadership skills. He was born on October 15, 1994, in Lahore, Pakistan. Babar is considered one of the top batsmen in modern cricket and has been a key player for the Pakistan cricket team. here are some highlights of Babar Azam’s cricketing achievements:
- Batting Excellence: Babar is known for his elegant batting style and solid technique. He has been a consistent run-scorer across formats and has gained a reputation for his ability to anchor an innings.
- Captaincy: Babar Azam was appointed as the captain of the Pakistan cricket team in all formats in late 2019. Under his leadership, Pakistan has shown potential and has aimed to build a competitive team.
- ODI and T20 Dominance: Babar has particularly excelled in One Day Internationals (ODIs) and Twenty20 Internationals (T20Is). He has been among the top run-scorers in both formats and has played match-winning innings for Pakistan.
- ICC Rankings: Babar has consistently been ranked among the top batsmen in ICC rankings for ODIs and T20Is.
- T20 Leagues: He has participated in various T20 leagues around the world, including the Pakistan Super League (PSL) and other international T20 tournaments.
- Youngest to 1000 T20I Runs: Babar Azam became the fastest Pakistani batsman to reach 1,000 runs in T20 Internationals.
- Consistency: His ability to adapt to different conditions and oppositions has contributed to his success as a top-order batsman.
- Records and Achievements: Babar has achieved various records and milestones during his career, showcasing his impact on Pakistan cricket.
- Future Potential: Babar Azam is seen as a potential future captain and a mainstay in the Pakistan batting lineup for years to come.
Babar Azam’s career and accomplishments may have evolved since then. For the most current and accurate information about his career, I recommend checking official cricket sources or news outlets.
David Warner is an Australian cricketer known for his aggressive batting style and explosive performances in limited-overs cricket. He was born on October 27, 1986, in Paddington, New South Wales, Australia. Warner is one of the most successful opening batsmen in modern cricket and has been a key player for the Australian cricket team. here are some highlights of David Warner’s cricketing achievements:
- Aggressive Batsmanship: Warner is known for his aggressive and attacking approach to batting. He is capable of scoring runs quickly and providing explosive starts in limited-overs formats.
- Limited-Overs Excellence: He has been particularly successful in limited-overs cricket, including One Day Internationals (ODIs) and Twenty20 Internationals (T20Is).
- Opening Batsman: Warner has been a mainstay at the top of the order for Australia in limited-overs cricket. His ability to take advantage of the fielding restrictions during the Powerplay overs has been crucial for his team.
- IPL Success: Warner has had a highly successful career in the Indian Premier League (IPL). He has captained the Sunrisers Hyderabad and has been one of the tournament’s leading run-scorers.
- Test Cricket: While his reputation is largely associated with limited-overs cricket, Warner has also performed well in Test cricket. He has scored several centuries and is known for his aggressive batting even in the longer format.
- Captaincy: Warner has been given leadership roles in both the Australian cricket team and various IPL teams due to his experience and cricketing acumen.
- Consistency: His ability to consistently deliver impactful performances, especially in white-ball cricket, has made him a valuable asset for Australia.
- Records and Achievements: Warner has achieved various records and milestones during his career, solidifying his status as one of Australia’s top batsmen.
- Comeback after Suspension: Warner, along with Steve Smith, returned to international cricket after serving a one-year suspension for his role in the ball-tampering scandal in 2018.
David Warner’s career and accomplishments may have evolved since then. For the most current and accurate information about his career, I recommend checking official cricket sources or news outlets.
Cheteshwar Pujara is an Indian cricketer known for his solid batting technique, patience, and ability to anchor the innings in Test cricket. He was born on January 25, 1988, in Rajkot, Gujarat, India. Pujara is considered one of the best Test batsmen in the world and has been a key player for the Indian cricket team in the longer format of the game. here are some highlights of Cheteshwar Pujara’s cricketing achievements:
- Test Cricket Specialist: Pujara is primarily known for his performances in Test cricket. He has earned a reputation as a classical Test batsman who excels in building long innings and wearing down bowlers.
- Batting Style: Pujara’s batting style is characterized by his solid defense, excellent judgment of deliveries, and the ability to accumulate runs patiently.
- Consistency: He has consistently been among the top run-scorers in Test cricket for India. Pujara’s ability to occupy the crease and bat for long periods of time has been instrumental in helping India set up and win Test matches.
- Overseas Performances: Pujara has performed well in overseas conditions, which is often considered a true test of a batsman’s skills. He has played pivotal roles in India’s Test victories abroad.
- Australia Tour: Pujara’s series-winning performances during India’s historic Test series victory in Australia in 2018-2019 were particularly noteworthy. He scored three centuries in that series.
- Number Three Batsman: Pujara often bats at the crucial number three position for India in Test cricket, providing stability to the batting lineup.
- Records and Achievements: He has achieved several records and milestones during his Test career, becoming one of India’s top run-scorers in the format.
- Team Player: Pujara’s ability to absorb pressure and bat for long periods of time has often allowed other aggressive batsmen to play their natural game around him.
Cheteshwar Pujara’s career and accomplishments may have evolved since then. For the most current and accurate information about his career, I recommend checking official cricket sources or news outlets.
Kumar Sangakkara is a former Sri Lankan cricketer who is widely regarded as one of the greatest wicketkeeper-batsmen in the history of the sport. He was born on October 27, 1977, in Matale, Sri Lanka. Sangakkara had a long and illustrious cricket career, and he is known for his elegant batting style, exceptional skills behind the stumps, and leadership qualities here are some highlights of Kumar Sangakkara’s cricketing achievements: 
- Batting Prowess: Sangakkara was a prolific run-scorer in all formats of the game. He had a stylish batting technique and the ability to play both aggressive and classical strokes.
- Wicketkeeper-Batsman: He was known for his dual role as a wicketkeeper and a top-order batsman. His skills behind the stumps made him one of the most complete players in the modern era.
- ODI and Test Cricket Success: Sangakkara achieved significant success in both One Day Internationals (ODIs) and Test cricket. He was a key player in Sri Lanka’s middle order and often played crucial innings in pressure situations.
- Record-Breaking Partnerships: Sangakkara was involved in numerous record-breaking partnerships with other Sri Lankan batsmen. He formed formidable batting partnerships with players like Mahela Jayawardene.
- Captaincy: Sangakkara captained the Sri Lankan cricket team in various formats. Under his leadership, Sri Lanka reached the final of the 2011 ICC Cricket World Cup and the ICC World Twenty20 in 2009.
- ICC Awards: He was named the ICC Cricketer of the Year and ICC Test Cricketer of the Year in 2012.
- Diverse Scorer: Sangakkara was known for his ability to score runs on a variety of pitches and conditions, making him a valuable asset in different parts of the world.
- Respected Figure: He was highly respected by fellow players, fans, and cricketing communities for his sportsmanship, intelligence, and articulate speeches.
- Post-Retirement Roles: After retiring from international cricket, Sangakkara continued to be involved in the sport as a cricket administrator, commentator, and cricketing ambassador.
Kumar Sangakkara’s post-retirement activities and any additional accomplishments after that date may not be included. For the most current and accurate information about his career and contributions, I recommend checking official cricket sources or news outlets.
AB de Villiers, also known as Abraham Benjamin de Villiers, is a former South African cricketer who is widely regarded as one of the most talented and innovative players in the history of the sport. He was born on February 17, 1984, in Pretoria, South Africa. De Villiers is known for his exceptional batting skills, versatility, and ability to play unconventional shots. here are some highlights of AB de Villiers’ cricketing achievements:
 Versatile Batsman: De Villiers was known for his ability to excel in all formats of the game, including Test cricket, One Day Internationals (ODIs), and Twenty20 cricket.
Versatile Batsman: De Villiers was known for his ability to excel in all formats of the game, including Test cricket, One Day Internationals (ODIs), and Twenty20 cricket.- Innovative Style: He was known for his innovative and unorthodox shot selection, which often left opponents and spectators amazed.
- ODI Records: De Villiers held several ODI records, including the fastest century in ODIs, which he achieved off just 31 balls. He was also one of the fastest players to reach 8,000, 9,000, and 10,000 runs in ODIs.
- Fielding Excellence: De Villiers was an outstanding fielder, known for his acrobatic and lightning-fast reflexes. He often fielded in close positions, and his athleticism saved numerous runs for South Africa.
- Captaincy: He served as the captain of the South African cricket team across formats. His leadership was marked by his aggressive and positive approach on the field.
- Retirement and Comeback: De Villiers announced his retirement from international cricket in 2018 but expressed interest in returning for the 2019 ICC Cricket World Cup. However, his comeback plans did not materialize.
- IPL Success: De Villiers played for the Royal Challengers Bangalore (RCB) in the Indian Premier League (IPL) and was one of the team’s most valuable players.
- Entertainment Value: He was known for adding entertainment and excitement to the game through his exceptional performances and creative shot-making.
- Crisis Management: De Villiers often rescued his team from difficult situations with his ability to accelerate the scoring rate and his composure under pressure
AB de Villiers’ post-retirement activities and any additional accomplishments after that date may not be included. For the most current and accurate information about his career and contributions, I recommend checking official cricket sources or news outlets.
Hashim Amla is a former South African cricketer known for his elegant batting style, solid technique, and remarkable consistency in all formats of the game. He was born on March 31, 1983, in Durban, South Africa. Amla was considered one of the finest batsmen of his generation and was highly respected for his cricketing skills and sportsmanship. here are some highlights of Hashim Amla’s cricketing achievements: 
- Elegant Batsmanship: Amla was known for his graceful batting style and textbook technique. He was particularly admired for his wristy play and his ability to time the ball perfectly.
- Records in Test Cricket: He held the record for being the fastest player to reach 2,000, 3,000, 4,000, 5,000, 6,000, 7,000, and 8,000 runs in Test cricket.
- Consistency: Amla’s ability to consistently score runs across all formats, especially in Test cricket, made him a reliable presence in the South African batting lineup.
- Captaincy: Amla served as the captain of the South African cricket team for a period of time. His calm and composed demeanor on the field reflected his leadership style.
- First South African to Score a Triple Century: In 2012, Amla became the first South African cricketer to score a triple century (311 not out) in Test cricket.
- ODI Performances: He was equally effective in One Day Internationals (ODIs), holding records for the fastest century and being among the leading run-scorers for South Africa.
- Humble Demeanor: Amla was highly respected by fellow players and fans for his humility, sportsmanship, and dignified conduct on and off the field.
- Muslim Identity: He was one of the few prominent Muslim cricketers in the international arena, and his presence was seen as an important representation of diversity in cricket.
- Retirement: Amla announced his retirement from international cricket in August 2019, leaving behind a legacy of excellence and contributions to South African cricket.
Hashim Amla’s post-retirement activities and any additional accomplishments after that date may not be included. For the most current and accurate information about his career and contributions, I recommend checking official cricket sources or news outlets.
Alastair Cook is a former English cricketer who is widely regarded as one of the greatest opening batsmen in the history of Test cricket. He was born on December 25, 1984, in Gloucester, England. Cook was known for his solid technique, patience, and remarkable ability to accumulate runs consistently. here are some highlights of Alastair Cook’s cricketing achievements:
- Test Cricket Career: Cook had a long and successful Test cricket career, representing England from 2006 to 2018. He was a mainstay at the top of the order and set several records during his tenure.
- Opening Batsman: Cook’s role as an opening batsman was crucial for England’s success. He was known for his ability to blunt the new ball and lay a strong foundation for the team.
- England’s All-Time Leading Run-Scorer: Cook holds the record for being England’s all-time leading run-scorer in Test cricket. He surpassed Graham Gooch’s record during his career.
- Captaincy: Cook served as the captain of the England cricket team from 2012 to 2017. Under his leadership, England achieved significant series victories and rose to the top of the Test rankings.
- Youngest English Centurion: Cook became the youngest English batsman to score a century on debut, achieving the feat against India in 2006.
- Centuries and Consistency: Cook scored numerous centuries throughout his Test career, showcasing his ability to convert starts into big scores. He was known for his concentration and patience at the crease.
- Ashes Success: Cook played a crucial role in England’s Ashes victories, both as a player and as a captain. He was known for his determined performances against arch-rivals Australia.
- Retirement: Cook announced his retirement from international cricket in 2018 after the Oval Test against India. His retirement marked the end of an era for English cricket.
- Respected Figure: Cook was highly respected by fellow players, fans, and cricketing communities for his dedication, character, and contributions to the sport.
Alastair Cook’s post-retirement activities and any additional accomplishments after that date may not be included. For the most current and accurate information about his career and contributions, I recommend checking official cricket sources or news outlets.
Sachin Tendulkar, often referred to as the “Little Master” or “Master Blaster,” is a former Indian cricketer and one of the greatest batsmen in the history of the sport. He was born on April 24, 1973, in Mumbai, India. Tendulkar is celebrated for his remarkable achievements, records, and his enduring impact on cricket. here are some highlights of Sachin Tendulkar’s cricketing achievements:
- Prolific Run-Scorer: Tendulkar is the highest run-scorer in international cricket history, amassing over 34,000 runs across all formats (Tests, One Day Internationals, and Twenty20 Internationals).
- Batting Excellence: He was known for his impeccable batting technique, balance, and a vast array of shots. Tendulkar could adapt to different formats and conditions.
- Century of Centuries: Tendulkar became the first player to score 100 international centuries, a testament to his consistency and longevity.
- Cricket World Cup Success: He played a pivotal role in India’s ICC Cricket World Cup victory in 2011. Tendulkar’s contributions were instrumental throughout the tournament.
- Longevity: Tendulkar enjoyed a career spanning over two decades, maintaining his form and impact over a long period of time.
- Youthful Debut: He made his Test debut for India at the age of 16, making him one of the youngest debutants in Test cricket history.
- Records and Milestones: Tendulkar holds numerous records, including being the highest run-scorer in Tests and ODIs, the most centuries in Tests and ODIs, and the most runs in World Cup history.
- Cultural Icon: Tendulkar’s popularity extended beyond cricket. He was a cultural icon in India and had a significant influence on cricket fans worldwide.
- Respect and Admiration: He was highly respected by fellow cricketers, opponents, and fans for his humility, sportsmanship, and contributions to the game.
- Bharat Ratna Award: In recognition of his immense contributions to Indian cricket, Tendulkar was awarded the Bharat Ratna, India’s highest civilian award.
- Retirement and Beyond: Tendulkar retired from international cricket in 2013. He has remained involved in various cricket-related activities, philanthropic work, and media engagements.
Sachin Tendulkar’s post-retirement activities and any additional accomplishments after that date may not be included. For the most current and accurate information about his career and contributions, I recommend checking official cricket sources or news outlets.
Brian Lara is a former West Indian cricketer who is widely regarded as one of the greatest batsmen in the history of the sport. He was born on May 2, 1969, in Santa Cruz, Trinidad and Tobago. Lara is known for his elegant batting style, aggressive strokeplay, and numerous records and accomplishments during his cricketing career. here are some highlights of Brian Lara’s cricketing achievements: 
- World Record Holder for Highest Individual Score: Lara holds the record for the highest individual score in Test cricket, having scored 400 not out against England in 2004. He also previously held the record with a score of 375 against the same team in 1994.
- Stylish Batsmanship: Lara was known for his stylish and graceful batting technique. He had the ability to play both classical shots and innovative strokes.
- Aggressive Playing Style: He was an aggressive batsman who could dominate bowlers with his powerful and artistic strokeplay.
- Test Cricket Success: Lara was a prolific run-scorer in Test cricket. He held the record for the most runs in Test cricket until it was surpassed by Sachin Tendulkar.
- ICC Awards: He was named the ICC Cricketer of the Year in 1995 and 1999, highlighting his impact on the global cricketing scene.
- Captaincy: Lara served as the captain of the West Indies cricket team at various points in his career. He was known for his leadership on and off the field.
- Triple Centuries in Test Cricket: Lara is one of only a few players to have scored multiple triple centuries in Test cricket.
- ODI Performances: While he was more renowned for his Test exploits, Lara also had several impactful performances in One Day Internationals (ODIs).
- Entertainment Value: Lara’s batting was not only effective but also entertaining, making him a fan-favorite around the world.
- Respected Figure: He was highly respected for his contributions to West Indian cricket and his ability to inspire fans with his performances.
Brian Lara’s post-retirement activities and any additional accomplishments after that date may not be included. For the most current and accurate information about his career and contributions, I recommend checking official cricket sources or news outlets.
Ricky Ponting is a former Australian cricketer and one of the most successful and accomplished players in the history of the sport. He was born on December 19, 1974, in Launceston, Tasmania, Australia. Ponting is known for his aggressive batting style, exceptional leadership skills, and contributions to Australian cricket. here are some highlights of Ricky Ponting’s cricketing achievements:
- Captaincy: Ponting was one of Australia’s most successful captains. He led the Australian cricket team during a period of dominance, winning multiple Test series and ICC tournaments, including two Cricket World Cups in 2003 and 2007.
- Batting Prowess: Ponting was a prolific run-scorer in all formats of the game. He was known for his powerful strokes, particularly his pull and hook shots.
- Test Cricket Success: He is considered one of the finest Test batsmen in history. Ponting held numerous records for most Test runs and centuries by an Australian until his retirement.
- ODI Performances: Ponting was also highly successful in One Day Internationals (ODIs). He was known for his aggressive approach and ability to anchor the innings.
- World Cup Glory: Ponting played a significant role in leading Australia to back-to-back ICC Cricket World Cup victories in 2003 and 2007.
- Fieldsman: He was an excellent fielder, known for his agility and safe catching in the slip cordon.
- Century of Centuries: Ponting became only the third player in history (after Sachin Tendulkar and Rahul Dravid) to score 100 international centuries across all formats.
- Respected Leader: He was highly respected by his teammates and opponents for his cricketing acumen and leadership qualities.
- Post-Retirement Roles: After retiring as a player, Ponting remained active in cricket. He worked as a cricket commentator, coach, and mentor for various teams.
- Hall of Fame Induction: Ponting was inducted into the ICC Cricket Hall of Fame in 2018, recognizing his outstanding contributions to the game.
Ricky Ponting’s post-retirement activities and any additional accomplishments after that date may not be included. For the most current and accurate information about his career and contributions, I recommend checking official cricket sources or news outlets.
Jacques Kallis is a former South African cricketer widely regarded as one of the greatest all-rounders in the history of the sport. He was born on October 16, 1975, in Cape Town, South Africa. Kallis was known for his exceptional batting skills, versatile bowling, and his impact in both Test and limited-overs cricket. here are some highlights of Jacques Kallis’s cricketing achievements:
- Batting Prowess: Kallis was one of the most prolific run-scorers in international cricket. He had a solid batting technique and could adapt his game to different formats and conditions.
- All-Round Abilities: Kallis was known for his all-round capabilities, excelling as a batsman and a seam bowler. His ability to contribute with both bat and ball made him a valuable asset to the team.
- Test Cricket Success: He was particularly dominant in Test cricket, where he scored over 10,000 runs and took more than 290 wickets. His performances helped shape South Africa’s success in the format.
- ODI Performances: Kallis was also effective in One Day Internationals (ODIs). He had a knack for playing crucial innings and was a key player in South Africa’s limited-overs campaigns.
- ICC Tournaments: He performed well in ICC Cricket World Cups and ICC Champions Trophy tournaments, contributing with both bat and ball.
- Fielding Excellence: Kallis was an outstanding fielder, known for his safe catching and agile movements in the slips and other fielding positions.
- Consistency: His ability to consistently perform across formats and for an extended period made him one of the most respected cricketers of his generation.
- Team Player: Kallis’s selfless approach to the game and his contributions to team success earned him the respect of teammates and opponents alike.
- Records and Achievements: He achieved numerous records and milestones during his career, solidifying his status as one of the all-time greats.
- Post-Retirement Roles: After retiring from international cricket, Kallis remained involved in the sport as a coach and mentor for various teams.
Jacques Kallis’s post-retirement activities and any additional accomplishments after that date may not be included. For the most current and accurate information about his career and contributions, I recommend checking official cricket sources or news outlets.
Michael Clarke is a former Australian cricketer who captained the Australian cricket team and was known for his stylish batting, leadership qualities, and contributions to the sport. He was born on April 2, 1981, in Liverpool, New South Wales, Australia. Clarke was a key player in the Australian cricket setup and had a significant impact on the team’s performances. here are some highlights of Michael Clarke’s cricketing achievements: 
- Captaincy: Clarke served as the captain of the Australian cricket team in all formats. He was known for his tactical acumen and ability to lead the team during challenging times.
- Stylish Batsman: Clarke was known for his elegant and stylish batting technique. He was a versatile batsman who could adapt his game to different formats and conditions.
- Test Cricket Success: Clarke’s performances in Test cricket were particularly noteworthy. He scored over 8,600 runs in Test matches and had a knack for performing in crucial situations.
- Ashes Victories: He led Australia to an Ashes series victory against England in 2013-2014. His performances during the series were instrumental in reclaiming the Ashes urn.
- ODI and T20 Cricket: Clarke also had success in One Day Internationals (ODIs) and Twenty20 Internationals (T20Is). He was a key player in Australia’s limited-overs campaigns.
- Batting Records: Clarke achieved numerous records and milestones during his career, including being among the leading run-scorers for Australia in international cricket.
- Respected Figure: He was respected by teammates and opponents for his cricketing skills and leadership qualities.
- Post-Retirement Roles: After retiring from international cricket, Clarke remained involved in the sport as a cricket commentator, expert analyst, and media personality.
- Philanthropic Efforts: Clarke has been involved in various charitable and philanthropic efforts aimed at giving back to the community.
Michael Clarke’s post-retirement activities and any additional accomplishments after that date may not be included. For the most current and accurate information about his career and contributions, I recommend checking official cricket sources or news outlets.
Martin Crowe was a former New Zealand cricketer who is widely regarded as one of the finest batsmen to have played for New Zealand. He was born on September 22, 1962, in Henderson, Auckland, New Zealand. Crowe was known for his elegant batting style, technique, and contributions to New Zealand cricket. He passed away on March 3, 2016, after battling cancer. Here are some highlights of Martin Crowe’s cricketing achievements: 
- Stylish Batsman: Crowe was known for his graceful and classical batting technique. He had the ability to play both aggressive and orthodox shots.
- Record-Breaking Captaincy: He captained the New Zealand cricket team during a period of transformation and success. Under his leadership, New Zealand achieved significant victories and improved their overall performance.
- Test Cricket Success: Crowe’s performances in Test cricket were particularly outstanding. He scored over 5,400 runs in Test matches and had a high average, showcasing his consistency and ability to play long innings.
- Innovative Approach: Crowe was known for his innovative thinking on and off the field. He introduced a new fielding position called “Crowe’s nest,” which placed a fielder close to the batsman’s end.
- ODI Contributions: He was also effective in One Day Internationals (ODIs), where he was known for his ability to anchor the innings and set up a platform for his team.
- Century Against Australia: Crowe scored a memorable century against Australia in the 1992 Cricket World Cup, helping New Zealand to victory.
- Influence on New Zealand Cricket: He had a significant impact on the development of cricket in New Zealand and played a crucial role in nurturing young talent.
- Post-Retirement Roles: After retiring from international cricket, Crowe remained involved in the sport as a cricket commentator, writer, and cricket administrator.
- Legacy: Martin Crowe is remembered as one of New Zealand’s cricketing legends, and his contributions to the game continue to be celebrated.






















 Versatile Batsman: De Villiers was known for his ability to excel in all formats of the game, including Test cricket, One Day Internationals (ODIs), and Twenty20 cricket.
Versatile Batsman: De Villiers was known for his ability to excel in all formats of the game, including Test cricket, One Day Internationals (ODIs), and Twenty20 cricket.























 पानी पूरी का व्यवसाय एक लोकप्रिय और आकर्षक विकल्प हो सकता है। यह व्यवसाय आपकी स्थानीयता, बाजार की मांग, और पानी पूरी की बिक्री के लिए स्थल के आधार पर बदलेगा।
पानी पूरी का व्यवसाय एक लोकप्रिय और आकर्षक विकल्प हो सकता है। यह व्यवसाय आपकी स्थानीयता, बाजार की मांग, और पानी पूरी की बिक्री के लिए स्थल के आधार पर बदलेगा। स्ट्रीट क्लोथिंग व्यवसाय का मतलब होता है कि आप सड़कों पर यातायात में होने वाले लोगों के लिए फैशन और कपड़ों की आपूर्ति प्रदान करते हैं। यह एक विशिष्ट वर्ग के ग्राहकों को लक्षित करने के लिए उनकी प्राथमिकताओं और फैशन चुनौतियों को समझने की कला है।
स्ट्रीट क्लोथिंग व्यवसाय का मतलब होता है कि आप सड़कों पर यातायात में होने वाले लोगों के लिए फैशन और कपड़ों की आपूर्ति प्रदान करते हैं। यह एक विशिष्ट वर्ग के ग्राहकों को लक्षित करने के लिए उनकी प्राथमिकताओं और फैशन चुनौतियों को समझने की कला है। एक व्यापारिक सेक्टर है जिसमें विभिन्न सौंदर्य उत्पादों की बिक्री की जाती है, जैसे कि स्किनकेयर, हेयरकेयर, मेकअप, आदि। यह एक व्यापारिक क्षेत्र है जो बहुत ही व्यापक है और ग्राहकों की बड़ी मांग है।
एक व्यापारिक सेक्टर है जिसमें विभिन्न सौंदर्य उत्पादों की बिक्री की जाती है, जैसे कि स्किनकेयर, हेयरकेयर, मेकअप, आदि। यह एक व्यापारिक क्षेत्र है जो बहुत ही व्यापक है और ग्राहकों की बड़ी मांग है।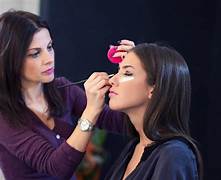 एक रुचिकर और सर्वप्रिय करियर विकल्प हो सकता है जिसमें आप व्यक्तियों के चेहरे की सौंदर्यिकता को बढ़ाने के लिए मेकअप और ब्यूटी तकनीकों का उपयोग करते हैं। यह एक रूप संवर्धन का कला है और आपके व्यक्तिगत और व्यावसायिक पौरुषों के आधार पर बदल सकता है।
एक रुचिकर और सर्वप्रिय करियर विकल्प हो सकता है जिसमें आप व्यक्तियों के चेहरे की सौंदर्यिकता को बढ़ाने के लिए मेकअप और ब्यूटी तकनीकों का उपयोग करते हैं। यह एक रूप संवर्धन का कला है और आपके व्यक्तिगत और व्यावसायिक पौरुषों के आधार पर बदल सकता है। एक ऐसा व्यवसाय है जिसमें आप उत्पादों या सेवाओं को ग्राहकों के द्वारा निर्दिष्ट स्थान तक पहुँचाते हैं। यह आजकल बहुत ही प्रसिद्ध और मांगी जाने वाली सेवा है, खासतर सामान की ऑनलाइन खरीदारी के बढ़ते प्रवृत्तियों के कारण।
एक ऐसा व्यवसाय है जिसमें आप उत्पादों या सेवाओं को ग्राहकों के द्वारा निर्दिष्ट स्थान तक पहुँचाते हैं। यह आजकल बहुत ही प्रसिद्ध और मांगी जाने वाली सेवा है, खासतर सामान की ऑनलाइन खरीदारी के बढ़ते प्रवृत्तियों के कारण।