-
Dec, Mon, 2023
Options Trading for Beginners
Option trading can be complex, but here’s a beginner’s guide to help you understand the basics:

What Are Options?
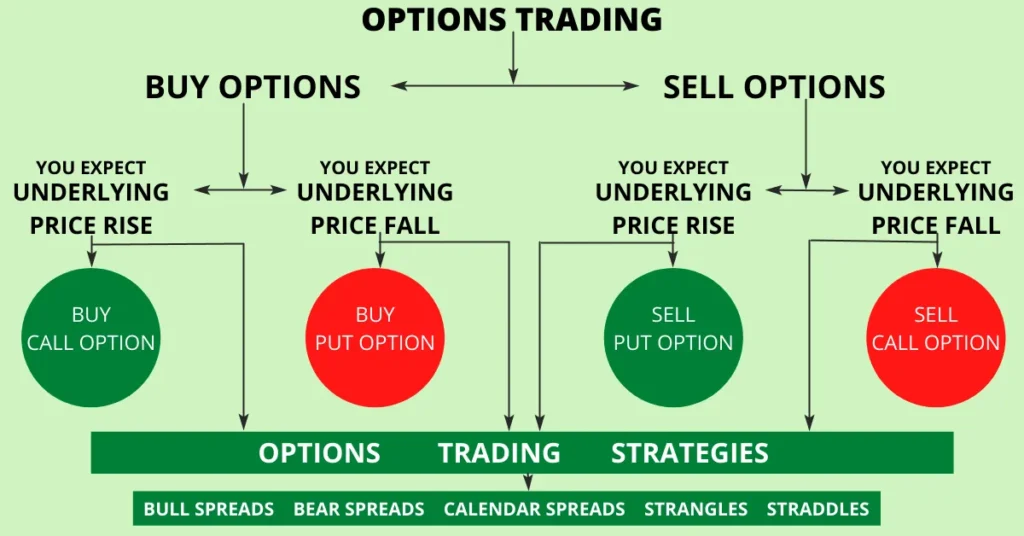
Options are financial derivatives that give you the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an underlying asset at a predetermined price (strike price) within a specified time frame. There are two primary types of options:
Call Options: These give you the right to buy the underlying asset at a specific price within a set time frame.
- Put Options: These give you the right to sell the underlying asset at a specific price within a set time frame.
Basic Option Terms:
- Underlying Asset: The stock, index, commodity, or currency the option is based on.
- Strike Price: The price at which the option holder can buy or sell the underlying asset.
- Expiration Date: The date when the option contract expires.
- Premium: The price paid for the option contract.
Strategies for Beginners:
Buying Call or Put Options (Long Options): This strategy involves purchasing call or put options depending on your market outlook. Calls are for bullish views, while puts are for bearish views.
Covered Call Strategy: For investors who hold the underlying asset, this strategy involves selling call options on that asset to generate income.
Cash-Secured Put: This involves selling put options while having enough cash to purchase the underlying asset if the option is exercised.
Tips for Beginners:
Educate Yourself: Understand the dynamics of options trading, including risks and rewards. Various online resources, books, and courses can help.
Start Small: Begin with a small amount of capital and trade low-cost options to limit potential losses while learning.
Use Stop-Loss Orders: Implement stop-loss orders to limit potential losses.
Practice with Simulators: Use paper trading or virtual platforms to practice trading without risking real money.
Diversify and Manage Risk: Don’t put all your funds into one trade. Diversify your portfolio and manage risk by not risking more than you can afford to lose.
Stay Updated: Keep track of market news, economic indicators, and events that might impact your options trades.
Risks:
Time Decay: Options have an expiration date, and their value decreases as the expiration date approaches.
Leverage: Options provide leverage, amplifying gains or losses, which can result in higher risk.
Market Volatility: High volatility can increase option prices, but it can also increase the risk.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Trading Options
The biggest advantage to buying options is that you have great upside potential with losses limited only to the option’s premium. However, this can also be a drawback since options will expire worthless if the stock does not move enough to be in-the-money. This means that buying a lot of out-of-the-money options can be costly.
Options can be very useful as a source of leverage and risk hedging. For example, a bullish investor who wishes to invest $1,000 in a company could potentially earn a far greater return by purchasing $1,000 worth of call options on that firm, as compared to buying $1,000 of that company’s shares. In this sense, the call options provide the investor with a way to leverage their position by increasing their buying power. On the other hand, if that same investor already has exposure to that same company and wants to reduce that exposure, they could hedge their risk by selling put options against that company.
The main disadvantage of options contracts is that they are complex and difficult to price. This is why options are often considered a more advanced investment vehicle, suitable only for experienced investors. In recent years, they have become increasingly popular among retail investors. Because of their capacity for outsized returns or losses, investors should make sure they fully understand the potential implications before entering into any options positions. Failing to do so can lead to devastating losses.
There is also a large risk selling options in that you take on theoretically unlimited risk with profits limited to the premium (price) received for the option.
Remember, options trading involves risks and requires careful consideration. It’s advisable to consult with a financial advisor or a professional before entering the options market, especially if you’re a beginner.